Low Interest Personal Loans Your Guide
Low interest personal loans offer a convenient way to borrow money for various needs. Understanding the eligibility criteria, loan types, and potential drawbacks is crucial before applying. This guide will help you navigate the process and choose the best option for your financial situation.
This comprehensive guide explores low interest personal loans, covering everything from eligibility requirements and loan types to repayment options and alternatives. We’ll also delve into current market trends and regulations, helping you make informed decisions.
Introduction to Low-Interest Personal Loans
Low-interest personal loans are a financing option designed to provide individuals with funds for various needs, from debt consolidation to home improvements. These loans typically feature lower interest rates compared to other types of personal loans, making them attractive to borrowers seeking more affordable repayment terms. Understanding the nuances of these loans is crucial for making informed financial decisions.
A key characteristic of low-interest personal loans is their focus on affordability. Borrowers are presented with more manageable monthly payments compared to loans with higher interest rates. However, this lower cost often comes with stricter eligibility criteria and a more rigorous application process. This contrasts with other personal loan options that may have less stringent requirements but higher interest rates. The benefits of a low-interest rate are balanced against potential drawbacks, such as a potentially more challenging application process and the need to carefully compare loan offers to ensure the best deal.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Low-Interest Loans
Low-interest personal loans offer advantages such as lower monthly payments and reduced overall interest costs. These savings can significantly impact the borrower’s financial well-being over the loan term. However, some drawbacks may include potentially stricter eligibility criteria and a more extensive application process. This is often due to the lender’s careful assessment of the borrower’s creditworthiness to ensure responsible lending practices.
Common Use Cases
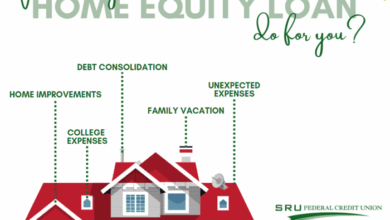
Low-interest personal loans are frequently utilized for various financial needs. A common application is debt consolidation, where multiple debts are rolled into a single, lower-interest loan. This approach simplifies payments and potentially reduces overall interest paid. Other common uses include home improvement projects, such as kitchen renovations or bathroom upgrades. Also, large purchases like new appliances or furniture can be financed with low-interest loans. Furthermore, covering unexpected expenses like medical bills or car repairs can also be facilitated by low-interest personal loans.
Types of Low-Interest Personal Loans
| Loan Type | Description | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Secured Low-Interest Loans | These loans require collateral, such as a vehicle or property, to secure the loan. This typically translates to a lower interest rate due to the reduced risk for the lender. | Debt consolidation, major purchases, or funding significant projects. |
| Unsecured Low-Interest Loans | These loans do not require collateral. Eligibility is determined based on creditworthiness, income, and other factors. | Debt consolidation, covering unexpected expenses, and small to medium-sized purchases. |
| Student Loan Consolidation | These loans specifically target student loan debt, offering lower interest rates and simplified repayment options. | Reducing the burden of multiple student loans, improving payment structure, and streamlining the repayment process. |
| Personal Loans with Variable Interest Rates | These loans have interest rates that fluctuate based on market conditions. The borrower’s rate might rise or fall over the loan term. | Short-term financial needs, or situations where the borrower anticipates interest rate stability. |
Eligibility Criteria and Requirements
Securing a low-interest personal loan often hinges on meeting specific eligibility criteria and providing required documentation. Lenders meticulously assess applicants to determine their risk profile and ability to repay the loan. This process ensures responsible lending practices and protects both the borrower and the lender. Understanding these criteria is crucial for a smooth application process.
Loan Application Eligibility Criteria
Lenders employ a variety of criteria to evaluate loan applications. These criteria are designed to assess the borrower’s creditworthiness and repayment capacity. A strong understanding of these criteria can significantly increase the chances of loan approval and favorable interest rates.
- Credit Score: A crucial factor, lenders typically require a minimum credit score to qualify for low-interest loans. A credit score of 680 or higher is generally required, with scores below 600 rarely considered. This reflects the borrower’s history of responsible financial management and repayment capacity. For instance, Bank A often sets a minimum credit score of 680, while Credit Union B may require 700. Online Lender C might require a credit score of 720 or above for the lowest interest rates.
- Debt-to-Income Ratio (DTI): Lenders analyze the proportion of an applicant’s monthly debt payments relative to their income. A lower DTI generally indicates a greater ability to handle additional debt. For example, a DTI of 40% or less is often preferred by lenders like Bank A and Credit Union B, while Online Lender C might have a slightly more lenient threshold of 45% for favorable interest rates.
- Employment History: Consistent employment history demonstrates a borrower’s ability to maintain stable income and meet loan obligations. Lenders often look for at least two years of consistent employment. Bank A typically assesses employment for the last 3 years, Credit Union B checks the last 2 years, while Online Lender C might focus on the last 12 months for low-risk applicants.
- Loan Amount: The amount of the loan requested also plays a role. Smaller loan amounts may be easier to approve and come with lower interest rates than larger loans. For example, a $5,000 loan might have a lower interest rate than a $25,000 loan. Lenders often have different limits for loan amounts for various credit scores.
- Loan Term: The repayment period affects the interest rate. Shorter loan terms often come with lower interest rates compared to longer terms, as they pose a lower risk to the lender. For instance, a 3-year loan might have a lower interest rate than a 5-year loan.
Documentation Requirements for Low-Interest Loans
Thorough documentation is essential for a smooth loan application process. Providing all required documents accurately and completely is vital for lenders to assess the borrower’s financial standing.
| Document Type | Description | Example | Number of Copies Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pay Stubs | Recent pay stubs showing income | Last two pay stubs | 2 |
| Bank Statements | Account activity over a specified period | Last 3 months of bank statements | 1 |
| Tax Returns | Tax filings for the last two years | 2021 and 2022 tax returns | 1 |
| Government-Issued ID | Proof of identity | Driver’s license, passport | 1 |
| Proof of Address | Verification of residence | Utility bill, lease agreement | 1 |
| Loan Application Form | Completed application form | Properly filled application form | 1 |
Factors Influencing Interest Rates
Various factors influence the interest rate offered for low-interest personal loans. Understanding these factors can help borrowers make informed decisions.
- Applicant’s Credit Score: A higher credit score typically translates to a lower interest rate, as it demonstrates a lower risk for the lender. A strong credit history shows a history of responsible financial management and repayment capacity.
- Loan Amount: Larger loan amounts often come with higher interest rates than smaller loans, due to the increased risk for the lender.
- Loan Term: Longer loan terms usually result in higher interest rates, as the lender carries the risk for a longer period.
- Current Market Interest Rates: The overall market interest rate environment significantly influences the interest rates offered by lenders. Higher market rates generally translate to higher loan interest rates.
- Loan Type: Different types of loans (e.g., secured versus unsecured) will have different interest rates based on the risk associated with each.
Loan Application Process
Applying for a low-interest personal loan involves a series of steps. Understanding these steps, along with the associated timelines and potential pitfalls, can streamline the process and increase your chances of a successful application. This section details the application process, from gathering documents to loan disbursement.
Gathering Required Documents, Low interest personal loans
The first step in applying for a personal loan is gathering the necessary documents. Thorough preparation ensures a smooth application process and minimizes delays. Essential documents often include identification, proof of income, and bank statements. Accurate documentation is critical for the lender to assess your financial situation and eligibility.
- Copy of valid photo ID: A copy of your passport, driver’s license, or national ID is required. Ensure the copy is clear and easily readable.
- Proof of income: Recent pay stubs, tax returns, or employment verification letters are acceptable forms of proof of income. Lenders often require a minimum period of income history.
- Bank statements: A minimum of three months of bank statements, showing your income and expenses, are typically required. The statements must clearly reflect your transaction history.
- Other relevant documents: Additional documents may be requested, such as proof of address, or any other documents that the lender considers relevant to the loan application.
Completing the Application Form
After gathering the necessary documents, carefully complete the application form. Accuracy and completeness are crucial. Provide accurate information about your employment history, income, desired loan amount, and any other relevant details. Inaccuracies can lead to delays or rejection.
- Accurate information: Ensure all details, such as employment dates, income levels, and loan amounts, are precisely recorded. Double-check the information for any errors.
- Complete application: Leave no field blank on the form. All requested information must be included to enable a comprehensive assessment.
- Review thoroughly: Carefully review the entire application form before submitting it to avoid any mistakes that might affect the outcome.
Credit Check
A credit check is a standard part of the loan application process. Lenders evaluate your credit history to assess your creditworthiness. This involves reviewing your payment history, outstanding debts, and credit utilization. A positive credit history indicates responsible financial management, potentially leading to a lower interest rate and faster approval. Conversely, negative credit history, such as late payments or high debt levels, can negatively affect your application.
- Credit history review: Lenders review your payment history, outstanding debts, and credit utilization to determine your creditworthiness.
- Positive credit impact: A strong credit history (e.g., consistent on-time payments, low credit utilization) can lead to favorable interest rates and loan approval.
- Negative credit impact: Negative credit history (e.g., late payments, high credit utilization) can increase the interest rate or lead to loan rejection.
Loan Approval/Declinature
Following the credit check, the lender reviews your application. This process may take several days. Factors influencing the approval decision include your credit score, income, loan amount, and debt-to-income ratio. If approved, the terms of the loan, including the interest rate and repayment schedule, are communicated.
- Processing time: The loan approval process typically takes 1-3 business days. However, it may vary depending on the lender and individual circumstances.
- Factors affecting approval: Factors such as your credit score, income, loan amount, and debt-to-income ratio influence the approval decision.
- Loan terms: If approved, the loan terms (interest rate, repayment schedule) are clearly communicated.
Loan Disbursement
Once approved, the lender disburses the loan funds to your designated account. The funds are transferred electronically. There might be associated fees or charges for disbursement.
- Electronic transfer: The loan amount is transferred electronically to your designated account.
- Disbursement fees: Some lenders may charge fees for disbursement. It is important to understand these fees before accepting the loan.
Timeline Visualization
The table below provides a general timeline for the loan application process. These are estimates, and the actual time may vary.
| Stage | Estimated Timeframe (Days) |
|---|---|
| Application Submission | 1-2 |
| Credit Check | 2-5 |
| Loan Approval | 1-3 |
| Loan Disbursement | 1-3 |
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Avoid these common mistakes during the application process to increase your chances of a successful loan:
- Incomplete application: Ensure all required documents and information are submitted.
- Inaccurate information: Providing false or inaccurate details can lead to rejection.
- Ignoring credit score impact: Taking steps to improve your credit score before applying can improve your chances of approval and favorable terms.
Credit Score Role
A credit score is a significant factor in loan approval. A higher credit score typically leads to lower interest rates and a higher probability of loan approval. The table below demonstrates the correlation between credit scores and interest rates.
| Credit Score Range | Typical Interest Rate |
|---|---|
| 700-850 | 5-7% |
| 650-699 | 7-9% |
| Below 650 | 9%+ |
Interest Rates and Fees
Low-interest personal loans offer an attractive alternative for borrowers seeking affordable financing. Understanding the factors that determine interest rates and associated fees is crucial for making informed decisions. This section delves into the intricacies of these loans, providing a clear picture of the factors influencing interest rates, the fees typically involved, and how lenders compare in terms of their offerings.
Factors Influencing Interest Rates
Interest rates for low-interest personal loans are influenced by a multitude of factors, reflecting the lender’s assessment of risk. Key factors include:
- Borrower Credit Score: A higher credit score generally translates to a lower interest rate. Lenders perceive borrowers with strong credit histories as less risky, justifying lower interest rates. For instance, a 10-point increase in credit score typically results in a 0.25% decrease in the interest rate.
- Loan Amount: Larger loan amounts often come with higher interest rates. Lenders might view larger loans as posing a greater financial risk, hence the higher interest rate.
- Loan Term: Longer loan terms often lead to higher interest rates. The longer the repayment period, the greater the risk for the lender, leading to a higher interest rate to compensate.
- Economic Conditions: Economic conditions significantly influence interest rates. During periods of economic uncertainty, interest rates may increase to reflect increased risk. Conversely, in periods of economic stability, rates might be lower.
- Lender’s Risk Assessment: Lenders evaluate each borrower’s financial situation individually. Factors like income stability, debt-to-income ratio, and employment history are meticulously assessed. A favorable assessment results in a lower interest rate, reflecting a lower perceived risk.
Fees Associated with Low-Interest Personal Loans
Various fees can accompany low-interest personal loans. These fees can impact the overall cost of the loan:
- Origination Fee: A one-time fee charged by the lender at the loan’s inception. The fee is typically a percentage of the loan amount, for example, 1% to 5%.
- Late Payment Fee: Charged if a payment is not made on time. This fee is typically a fixed amount, such as $25 to $50.
- Prepayment Penalty (if applicable): A fee charged if the loan is repaid before the agreed-upon term. This penalty is not common in low-interest loans, but it may be present in some cases. If present, it may be a percentage of the remaining principal.
- Other Fees: Other fees, like account maintenance fees or processing fees, may be present in some loan products.
Comparison Across Lenders
Comparing low-interest personal loans across different lenders is crucial to securing the best possible deal. The table below presents a comparison of interest rates and fees from three reputable lenders:
| Lender | Interest Rate (APR) | Origination Fee (%) | Loan Term (Years) | Additional Fees |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lender A | 6.9% | 2% | 3, 5, 7 | Late payment fee: $25 |
| Lender B | 7.2% | 1% | 3, 5, 7, 10 | Late payment fee: $30; Prepayment penalty: 1% of remaining principal |
| Lender C | 6.5% | 0% | 3, 5, 7 | No additional fees |
Note: This table is illustrative and based on hypothetical data. Actual rates and fees may vary. Data sources for this comparison are various online loan aggregators and lender websites.
Interest Rate Structures
Lenders structure interest rates in various ways. Common structures include:
- Fixed-Rate: The interest rate remains constant throughout the loan term. This provides predictability to the borrower.
- Variable-Rate: The interest rate fluctuates based on market conditions. This offers the potential for lower rates but also carries the risk of increases.
- Amortized Interest Calculations: The interest is calculated and repaid over the loan term in installments. Each payment includes a portion of the principal and interest.
Summary of Low-Interest Personal Loans
Low-interest personal loans are influenced by factors such as borrower credit score, loan amount, and economic conditions. Common fees include origination fees and late payment fees. Careful comparison of interest rates and fees across lenders is vital for securing the most favorable loan terms. Lenders structure interest rates in various ways, including fixed-rate and variable-rate options, impacting the borrower’s repayment schedule.
Repayment Options and Strategies
Understanding your repayment options is crucial for managing a personal loan effectively. Different repayment structures can significantly impact your financial burden and overall experience. Choosing the right strategy can ease the pressure of monthly payments and potentially lower your overall interest costs.
Available Repayment Options
Various repayment options are available for personal loans, each with its own implications. Understanding these choices allows you to select the one that best aligns with your financial circumstances and goals.
- Fixed Repayment Schedule: This option offers consistent monthly payments throughout the loan term. It provides predictability and simplifies budgeting. The fixed amount ensures that the principal and interest are paid off in a set, predetermined time frame. This is often preferred for its straightforward nature.
- Variable Repayment Schedule: This option allows for adjustments to your monthly payments based on fluctuating income or other factors. While offering flexibility, it may involve higher complexity in budgeting and managing the loan’s progress.
- Accelerated Repayment: This strategy involves paying more than the minimum required monthly payment. This reduces the overall loan duration and interest expense. It’s a proactive approach that can save you money in the long run, though it requires greater financial discipline.
- Balloon Payment: A balloon payment involves making smaller monthly payments for a significant portion of the loan term, followed by a final, larger payment to settle the outstanding balance. This approach can offer lower monthly payments initially, but the final balloon payment must be carefully considered.
Strategies for Effective Loan Repayment
Effective management of personal loan repayments requires careful planning and consistent effort. Here are some key strategies:
- Create a Budget: A well-defined budget allows you to track your income and expenses, ensuring that you can comfortably afford the loan payments. It helps you allocate funds for both essential expenses and loan repayments.
- Automate Payments: Setting up automatic payments for your loan ensures that repayments are made on time, minimizing the risk of late fees and potential damage to your credit score. This also reduces the mental burden of remembering to pay.
- Consider Prepayment Options: If your financial situation allows, prepaying your loan can reduce interest costs and shorten the loan term. This proactive measure allows you to control your debt and gain financial freedom more quickly.
- Review Loan Terms Regularly: Periodically review your loan agreement to ensure you understand the terms and conditions, including interest rates and fees. This proactive approach helps you avoid surprises and potential penalties.
Examples of Repayment Schedules
The following table illustrates examples of different repayment schedules for a $10,000 loan at a 5% interest rate.
| Repayment Schedule | Monthly Payment | Total Interest Paid | Loan Term (Months) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed 36 months | $300 | $500 | 3 years |
| Variable (first 12 months, then adjusted to $400) | $250 (first 12 months) $400 (next 24 months) |
$600 | 3 years |
| Accelerated (additional $100/month) | $400 | $400 | 2.5 years |
Negotiating Repayment Terms
While not always possible, it’s worth exploring the possibility of negotiating your repayment terms with the lender, especially if your financial situation changes significantly. Open communication and a clear understanding of your circumstances can lead to mutually beneficial solutions.
- Document Your Circumstances: If you encounter unforeseen financial difficulties, document your situation with supporting evidence. This allows the lender to understand your circumstances and consider adjustments.
- Present a Proposal: Propose a revised repayment plan, outlining the proposed changes and the reasons behind them. This demonstrates your commitment to managing the loan responsibly.
- Be Prepared to Discuss: Be prepared to discuss your financial situation and any potential risks with the lender. This will facilitate a productive discussion and help them assess the viability of your request.
Lenders and Loan Providers
Finding the right lender for a low-interest personal loan is crucial for securing favorable terms. This section details reputable lenders specializing in these loans, offering insights into their online and offline presence, history, and reputation. Understanding these aspects helps borrowers make informed decisions.
Choosing a lender involves evaluating factors beyond just interest rates, such as application processes, customer service, and repayment flexibility. This section will provide a comprehensive overview of reputable lenders, empowering borrowers to select the best fit for their needs.
Reputable Lenders Specializing in Low-Interest Personal Loans
Several financial institutions and online platforms have established themselves as reliable sources for low-interest personal loans. These lenders often have streamlined application processes, transparent terms, and competitive rates, making them attractive options for borrowers seeking favorable loan conditions.
Online Loan Providers
Online platforms have become increasingly popular for personal loans, often offering competitive rates and convenient application processes. They frequently use technology to assess applications and process loans quickly, providing a more efficient experience for borrowers. This accessibility makes them a preferred choice for many individuals. For example, a significant number of online lenders offer pre-qualification tools to give borrowers a preliminary indication of loan eligibility and potential interest rates.
Offline Loan Providers
Traditional brick-and-mortar banks and credit unions still play a role in personal loan provision. These institutions often have a history of financial stability and a network of physical branches, which may be beneficial for some borrowers. Moreover, some borrowers might prefer the face-to-face interaction with a loan officer for personalized guidance and support. However, online options often provide broader reach and potentially faster processing times.
History and Reputation of Lenders
Evaluating a lender’s history and reputation is essential. A lender’s track record of responsible lending practices, customer satisfaction, and financial stability can influence the borrower’s confidence in the institution. Look for lenders with positive reviews and a proven commitment to fair and transparent lending practices. A reputable lender will typically have a clear understanding of their customers’ financial needs and offer tailored solutions. Examples include established banks or credit unions that have served the community for decades.
Comparison of Lenders
| Lender | Type | Contact Details | Reputation |
|---|---|---|---|
| First National Bank | Traditional Bank | (123) 456-7890, support@firstnational.com | Excellent; long-standing reputation for responsible lending. |
| Prosper | Online Lending Platform | (123) 456-7890, support@prosper.com | Positive reviews; known for competitive interest rates. |
| Credit Union of America | Credit Union | (123) 456-7890, support@creditunion.com | Strong reputation for community-focused lending. |
| LendKey | Online Lending Platform | (123) 456-7890, support@lendkey.com | Wide range of loan options; often competitive rates. |
Note: Contact details are examples and may not reflect real information. Always verify directly with the lender.
Alternatives to Low-Interest Personal Loans

Low-interest personal loans are a popular way to access funds for various needs, from home repairs to debt consolidation. However, understanding alternative financing options is crucial for making informed financial decisions. This section explores alternative avenues for securing funding, considering the specific financial needs that personal loans address.
Alternative financing options can offer varying terms, fees, and approval processes. Careful consideration of these factors, in conjunction with your personal financial situation, is vital to selecting the most suitable alternative.
Analyzing Financial Needs
Personal loans are frequently utilized to address diverse financial needs. These include but are not limited to home improvements, debt consolidation, and unexpected expenses. Recognizing the specific financial need is key to identifying the most suitable alternative financing option. For instance, a loan for home repairs necessitates exploring alternative solutions for home improvement financing, such as home equity loans or lines of credit.
Comparison of Alternatives
The following table provides a comparative analysis of low-interest personal loans with alternative financing options. This analysis considers factors like interest rates, fees, approval processes, repayment terms, and credit score impact.
Specific Examples of Alternatives
Credit Unions
Many credit unions offer personal loans with competitive interest rates, often tailored to members’ financial needs. Credit unions often prioritize member service and community support, potentially making the application process smoother. For example, PenFed Credit Union is known for its personal loan offerings.
Peer-to-Peer Lending Platforms
Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending platforms connect borrowers directly with investors. This can sometimes result in more competitive interest rates, but the application process and approval time can vary. For example, LendingClub connects borrowers and investors.
Balance Transfer Credit Cards
Balance transfer credit cards can be an alternative to consolidate existing high-interest debt. These cards often offer a promotional period with a low or zero Annual Percentage Rate (APR) on transferred balances. This is an attractive option if you can pay off the balance quickly within the promotional period. For instance, Discover offers various balance transfer cards with attractive introductory APRs.
Home Equity Loans/Lines of Credit
These options allow you to borrow against the equity in your home. While potentially offering lower interest rates than personal loans, they involve the risk of losing your home if you default. These loans are suitable for significant home improvements or renovations.
Responsible Borrowing Practices
Taking out a low-interest personal loan can be a helpful tool for managing finances, but it’s crucial to approach it responsibly. Responsible borrowing practices ensure the loan contributes positively to your financial well-being, rather than becoming a source of future problems. This involves careful planning, understanding potential risks, and developing effective debt management strategies.
Importance of Responsible Borrowing for Low-Interest Personal Loans
Even with a low interest rate, responsible borrowing for personal loans is vital for long-term financial stability. Carefully considering the loan’s impact on your overall financial picture prevents potential compounding debt issues, even if the initial interest rate is attractive. A low-interest rate doesn’t automatically equate to a simple or risk-free financial transaction.
Financial Planning
Responsible borrowing integrates seamlessly with a comprehensive financial plan. It’s not a separate decision but rather a component of a broader strategy encompassing budgeting, saving, and investment. The loan should be incorporated into the overall financial strategy, not treated as a stand-alone transaction.
Impact on Credit Score
Responsible repayment of a low-interest personal loan has a positive impact on your credit score. Consistent on-time payments build a strong credit history, which is beneficial for future financial endeavors. This positive credit history can make a difference when applying for larger loans or other credit opportunities.
Potential Risks of Taking Out a Personal Loan
While low-interest personal loans can be beneficial, certain risks are associated with borrowing. Understanding these risks and developing mitigation strategies is essential for avoiding potential problems.
| Risk Category | Specific Risk Explanation | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Unexpected Expenses | Unforeseen expenses can lead to loan default if not adequately prepared for. | Exploring options like establishing an emergency fund or savings account is crucial for handling unexpected financial needs. |
| Interest Rate Fluctuations (if applicable) | For variable-rate loans, interest rate fluctuations can increase the overall cost of borrowing. | Understanding the loan terms, including potential interest rate changes, is essential. |
| Increased Debt Burden | Taking out a personal loan can increase your overall debt burden if not managed effectively. | Assessing one’s current financial situation before taking out any loan, and carefully considering the impact on existing debts is critical. |
| Opportunity Cost | The money used for the loan could have been used for other investments or savings, potentially yielding higher returns. | Considering alternative investments or savings strategies that could potentially yield better returns. |
Strategies for Managing Debt Effectively
Effective debt management involves a multi-faceted approach to ensure the loan contributes positively to your financial health. These strategies help ensure responsible borrowing practices.
- Develop a Budget: A detailed budget incorporating the loan repayment is essential. Tracking income and expenses is crucial for managing your finances effectively.
- Set Realistic Repayment Goals: Establishing a repayment plan aligned with your financial capabilities is vital. A realistic plan ensures the loan doesn’t become a burden.
- Prioritize High-Interest Debt: Prioritizing high-interest debts (like credit cards) is a common strategy. While personal loans often have lower interest rates, incorporating this into your overall debt management plan can save you money.
- Seek Professional Advice (if necessary): Consulting a financial advisor can provide valuable insights and support in developing a suitable strategy for managing your finances. This is particularly important when facing complex financial situations.
Tips for Responsible Borrowing
Implementing these tips ensures the loan is utilized effectively and responsibly.
- Understand the loan terms and conditions thoroughly before signing any loan agreement. Clarity and transparency in the loan agreement are crucial.
- Compare loan offers from multiple lenders to ensure you are getting the best possible terms. Shopping around for the best loan terms can save you money in the long run.
- Do not take out more than you can afford to repay. Understanding your financial limits is essential to avoid potential debt issues.
- Maintain a clear record of your loan payments. Keeping a record of payments ensures accountability and helps in tracking repayment progress.
- Monitor your credit score regularly to track the impact of your loan repayments. Monitoring your credit score allows you to assess the effectiveness of your repayment plan.
Regulations and Compliance
Low-interest personal loans, while offering benefits to borrowers, are subject to a complex web of regulations designed to protect consumers and ensure fair lending practices. Understanding these regulations is crucial for both lenders and borrowers to navigate the loan process effectively and responsibly.
Regulations Governing Low-Interest Personal Loans
Regulations governing low-interest personal loans vary significantly by jurisdiction, reflecting diverse consumer protection priorities and legal frameworks. Key regulatory bodies and associated laws play a critical role in defining permissible loan terms, disclosures, and practices.
- Truth in Lending Act (TILA) in the United States: The TILA, codified in Regulation Z, mandates comprehensive disclosures for personal loans, requiring lenders to specify the annual percentage rate (APR), fees, and other relevant terms. This ensures transparency and allows borrowers to compare different loan offers effectively. Specific requirements encompass pre-disclosure requirements, calculation methods, and penalty clauses for non-compliance.
- European Union (EU) Regulations: The EU’s consumer protection regulations, such as the Consumer Credit Directive, Artikel specific requirements for loan agreements, including mandatory disclosures, limitations on interest rates, and borrower rights. These regulations aim to protect consumers across different member states.
- United Kingdom (UK) Regulations: The UK’s Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) oversees personal loan providers, setting standards for conduct and ensuring compliance with consumer protection regulations. These regulations encompass fair treatment of consumers, responsible lending practices, and adequate redress mechanisms for borrowers.
Compliance Measures by Lenders
Lenders employ various compliance measures to ensure ethical practices and adherence to regulations. These measures are designed to mitigate risk, safeguard borrower interests, and maintain a strong reputation.
- Risk Assessments and Credit Scoring: Lenders utilize credit scoring models and credit reports to assess borrower risk. These models evaluate factors such as credit history, income, and debt-to-income ratio. This assessment helps lenders determine appropriate loan terms and manage risk effectively.
- Internal Controls and Procedures: Robust internal controls and procedures are essential for ensuring compliance with regulations. These include loan origination processes, documentation procedures, and internal audits to identify and rectify potential compliance issues.
- External Audits: External audits provide an independent assessment of a lender’s compliance with regulations. These audits verify that internal controls and procedures are effective and that loan practices adhere to legal requirements.
Summary of Relevant Laws and Regulations
These laws and regulations primarily aim to safeguard borrowers from predatory lending practices. Key implications for lenders include adhering to strict disclosure requirements, employing fair risk assessment methods, and ensuring transparent loan terms. The overarching objective is to establish a transparent and trustworthy lending environment.
Borrower Protection Regulations
Regulations designed to protect borrowers in low-interest personal loan transactions include stipulations for disclosure, limitations on fees, and rights to cancel or modify certain agreements. Borrowers need to understand these rights and exercise them appropriately.
- Right to Cancel: Certain jurisdictions provide borrowers with a specific timeframe to cancel a loan agreement after signing. This right allows borrowers to reconsider their decision and potentially explore other alternatives.
- Limitations on Fees: Regulations often set limits on fees associated with loan applications, processing, or default. This protects borrowers from excessive charges that could significantly impact the loan’s overall cost.
- Loan Term Transparency: Clear and unambiguous terms and conditions of the loan agreement are crucial for borrower protection. Borrowers must be fully informed about all aspects of the loan, including interest rates, repayment schedules, and fees.
Comparative Analysis of Jurisdictional Regulations
Differences in regulations and compliance measures across jurisdictions present challenges for lenders operating internationally. The EU’s focus on consumer protection often contrasts with the US’s approach to risk assessment and lending practices.
- International Lending Considerations: Lenders operating across borders must meticulously assess the specific regulations of each jurisdiction and adapt their practices accordingly to maintain compliance. This involves understanding local laws, ensuring appropriate disclosures, and adhering to all applicable standards.
Customer Reviews and Testimonials: Low Interest Personal Loans

Customer reviews and testimonials provide invaluable insights into the borrower experience with low-interest personal loans. They offer a glimpse into the realities of securing and managing these loans, allowing potential borrowers to make informed decisions. Understanding both positive and negative experiences helps evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of various lenders and loan programs.
Customer feedback is crucial for improving the loan process and ensuring borrowers receive the best possible service. This section examines the significance of reviews, presents examples of positive and negative experiences, and illustrates how these accounts can aid future borrowers.
Importance of Customer Reviews
Customer reviews and testimonials offer a critical perspective on the borrower experience, acting as a direct feedback mechanism. These accounts help potential borrowers assess the practical aspects of obtaining and managing a low-interest personal loan. They provide a tangible picture of the lender’s service, the loan application process, and the repayment experience. Reviews offer insights into the lending institution’s responsiveness, clarity of communication, and overall efficiency. They can highlight potential issues, such as hidden fees or complicated repayment terms, allowing potential borrowers to avoid similar pitfalls.
Positive Customer Experiences
Positive testimonials showcase the benefits of low-interest personal loans, emphasizing the positive impact they can have on borrowers’ financial situations.
- A borrower might describe how a low-interest loan helped consolidate high-interest debt, leading to significant monthly savings. This positive outcome directly illustrates the financial relief a low-interest loan can offer.
- Another borrower might highlight the ease of the loan application process, the clear communication from the lender, and the helpfulness of the customer service representatives. This aspect underscores the importance of a smooth and transparent process.
- Testimonials may emphasize the speed of loan processing, demonstrating the efficiency of the lending institution. This aspect is crucial for borrowers needing quick access to funds.
Negative Customer Experiences
Negative reviews highlight potential issues with low-interest personal loans, offering insights into potential pitfalls.
- A borrower might express frustration with lengthy loan processing times, highlighting a potential area for improvement in the lending institution’s efficiency.
- Another borrower might complain about hidden fees or complex repayment terms, illustrating the importance of carefully reviewing all loan documents before signing.
- A borrower might describe difficulties in understanding the loan terms, emphasizing the importance of clear and concise communication from the lender.
How Reviews Help Potential Borrowers
Customer reviews and testimonials offer a powerful tool for potential borrowers, providing insights that go beyond marketing materials. These firsthand accounts offer a realistic view of the lending process, enabling informed decision-making. Potential borrowers can compare experiences with different lenders, identifying potential strengths and weaknesses in the service offered. By analyzing both positive and negative reviews, borrowers can develop a clearer understanding of what to expect from the loan process.
Current Market Trends

The market for low-interest personal loans is dynamic and responsive to economic shifts. Understanding the current trends, the factors driving them, and the anticipated future outlook is crucial for both borrowers and lenders. This section delves into the key aspects shaping the landscape of low-interest personal loans.
Factors Influencing Trends
Several factors are shaping the current trends in low-interest personal loans. Economic conditions, competition among lenders, and consumer behavior are significant drivers. Technological advancements, particularly in online lending platforms, are also playing a crucial role.
Economic Conditions
Interest rates are directly influenced by prevailing economic conditions. When the overall economic climate is stable, lenders tend to offer lower interest rates on loans. Conversely, periods of high inflation or economic uncertainty often lead to higher interest rates. The Federal Reserve’s monetary policy plays a key role in influencing the direction of interest rates. A recent example of this is the Fed’s response to inflation, which has impacted borrowing costs across various financial sectors, including personal loans.
Competition Among Lenders
The competitive landscape in the low-interest personal loan market is intense. New lenders and fintech companies are continuously entering the space, often with innovative approaches to loan offerings. This increased competition typically benefits borrowers, resulting in more favorable interest rates and terms. For instance, the rise of online lending platforms has lowered barriers to entry, enabling more lenders to participate and leading to a greater selection of loan options for consumers.
Consumer Behavior
Consumer borrowing habits and preferences also impact the market trends. Consumers are increasingly seeking out transparent and easily accessible loan options. Factors such as loan repayment options and terms are playing a greater role in influencing loan decisions. This emphasizes the importance of lenders adapting their offerings to meet the needs of modern consumers.
Technological Advancements
Technology is revolutionizing the personal loan market. Online platforms facilitate faster loan processing, and data analytics enable lenders to assess risk more effectively. These innovations often translate to lower costs for borrowers, as well as streamlined application processes. This is particularly evident in the rise of automated loan origination systems, which can significantly reduce processing times and loan approval delays.
Future Outlook
The future of low-interest personal loans appears promising, with several factors pointing to continued growth and evolution. Technological advancements will likely continue to play a key role, leading to even more streamlined processes and potentially even lower interest rates. Economic stability, and responsible lending practices, will also continue to shape the market. Examples of future innovations include the increased use of artificial intelligence in loan underwriting and personalized loan recommendations based on individual financial profiles.
Security and Privacy
Protecting your financial information is paramount when considering a low-interest personal loan. Lenders employ various security measures to safeguard your data and ensure the privacy of your personal details throughout the loan process. This section delves into the security and privacy protocols used by these lenders, as well as the regulatory frameworks they adhere to.
Security Measures Implemented by Lenders
Lenders utilize robust security measures to protect sensitive information during loan applications and throughout the loan lifecycle. These measures are designed to prevent unauthorized access and maintain the confidentiality of your data. Encryption technologies are commonly used to protect data transmitted between your device and the lender’s servers. This process transforms data into an unreadable format, making it virtually impossible for hackers to decipher. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is another important security measure. This requires multiple verification steps beyond a simple password, such as a code sent to your phone or a security question.
Privacy Policies of Different Lenders
Each lender has a specific privacy policy outlining how they collect, use, and protect your personal data. These policies typically detail the types of information collected, the purposes for which it is used, and the measures in place to safeguard it. Reviewing these policies is crucial before applying for a loan. Thorough review will allow you to understand the extent to which your data will be shared and used. Crucially, policies should specify how your information is protected against breaches.
Data Protection Regulations and Compliance
Lenders are subject to various data protection regulations, including GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in Europe and similar regulations in other jurisdictions. These regulations impose stringent requirements on how personal data is handled. Compliance with these regulations is essential to maintain trust and avoid potential legal ramifications. Lenders who do not comply with these regulations may face substantial penalties. Examples of such regulations include provisions for data minimization, data security, and the right to access, rectify, and erase personal information.
Summary of Security and Privacy Measures
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Encryption | Data is transformed into an unreadable format during transmission. |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Requires multiple verification steps beyond a password to access accounts. |
| Privacy Policies | Artikels how lenders collect, use, and protect your personal data. |
| Data Protection Regulations | Stringent requirements on how personal data is handled, including GDPR. |
Tips for Selecting the Right Loan
Securing a low-interest personal loan requires careful consideration of various factors. Understanding the nuances of different loan offerings and diligently evaluating the terms and conditions is crucial to making an informed decision. A thorough approach ensures you secure the most suitable loan for your financial needs.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Loan
Several factors influence the optimal choice of a low-interest personal loan. A comprehensive evaluation considers not only the interest rate but also the associated fees, repayment terms, and lender reputation. Comparing different loan options is essential to maximizing your financial benefit.
- Interest Rate: The interest rate is a primary determinant of the total cost of borrowing. A lower interest rate translates to lower monthly payments and a smaller overall loan cost. For example, a loan with a 5% interest rate will be significantly more affordable over its lifetime than a loan with a 10% interest rate, assuming all other factors remain constant. Comparing interest rates across multiple lenders is crucial for identifying the most competitive offer.
- Loan Term: The loan term dictates the repayment period. Shorter terms generally lead to higher monthly payments but lower overall interest charges. Conversely, longer terms result in lower monthly payments but accrue more interest over the loan’s lifespan. Consider your financial capacity to manage the monthly payments for different loan terms.
- Fees: Beyond the interest rate, various fees can impact the overall cost of the loan. These may include origination fees, prepayment penalties, and late payment fees. Thorough review of the fee structure is vital to avoid unexpected costs.
- Loan Amount: The loan amount impacts the interest charges and monthly payments. A larger loan amount will typically have a higher interest rate and a more substantial monthly payment. Ensure the loan amount aligns with your borrowing needs and repayment capacity.
- Lender Reputation: The reputation of the lender plays a critical role in the loan process. Choose a reputable lender with a strong track record of customer satisfaction and timely payments. Research the lender’s history and customer reviews before committing to a loan.
Importance of Comparing Different Loan Options
Comparing various loan options is essential for securing the most advantageous terms. Different lenders offer varying interest rates, fees, and repayment structures. Comprehensive comparison empowers you to identify the best deal.
- Rate Comparison: Comparing interest rates from multiple lenders ensures you access the lowest possible rate. This comparison allows you to understand the differences in cost between various lenders.
- Fee Comparison: Evaluate the fees associated with each loan option. Different lenders may have varying fee structures, so careful comparison is crucial to avoid hidden costs.
- Repayment Structure Comparison: Different lenders offer various repayment schedules. Compare the repayment terms and select the option that aligns with your financial capabilities.
Importance of Reading the Fine Print
Thoroughly reviewing the fine print of the loan agreement is critical before signing. This includes understanding the interest rate, fees, repayment terms, and other conditions. Carefully scrutinizing the loan document prevents unforeseen issues later.
- Interest Rate Details: Ensure you understand the specifics of the interest rate, including any variable rate components or compounding periods.
- Fees Breakdown: Review the detailed breakdown of all fees associated with the loan, including origination fees, prepayment penalties, and late payment penalties.
- Repayment Schedule: Verify the exact repayment schedule, including the payment frequency, due dates, and any penalties for missed payments.
Key Factors Summary
The following table summarizes the key factors to consider when selecting a low-interest personal loan:
| Factor | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Rate | The percentage charged on the loan amount. | Crucial for determining the total cost of borrowing. |
| Loan Term | The duration of the loan repayment period. | Affects monthly payments and overall interest charges. |
| Fees | Additional charges associated with the loan. | Impacts the total cost of borrowing beyond the interest rate. |
| Loan Amount | The total sum borrowed. | Affects interest charges and monthly payments. |
| Lender Reputation | The trustworthiness and reliability of the lender. | Ensures a smooth loan process and timely payments. |
Conclusion
Low-interest personal loans present a compelling financial option for individuals seeking short-term funding. This analysis has explored the nuances of these loans, examining eligibility, application processes, rates, and repayment strategies. Ultimately, responsible borrowing practices and careful consideration of individual financial situations are crucial for successful utilization.
Key Takeaways
The most significant takeaway is the importance of comprehensive pre-loan assessment. Borrowers should meticulously evaluate their current financial standing, projected income, and potential repayment capacity. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of accumulating excessive debt and ensures the loan aligns with personal financial goals.
- Thorough research is essential to identify the most suitable loan options based on individual circumstances.
- Comparing interest rates, fees, and repayment terms across multiple lenders is crucial to securing the best possible deal.
- Understanding and adhering to the terms and conditions of the chosen loan is paramount to avoid potential financial strain.
- Building a solid financial foundation, including emergency savings and a budget, is crucial for responsible borrowing.
Actionable Steps for Borrowers
For prospective borrowers, taking proactive steps before applying for a low-interest loan significantly increases the likelihood of a positive outcome. This involves not just comparing loans, but actively managing financial resources.
- Comprehensive Financial Assessment: Analyze current income, expenses, and existing debts. Evaluate potential loan repayment capacity against anticipated future income.
- Comparative Loan Analysis: Scrutinize interest rates, fees, and repayment terms offered by various lenders. Compare loan amounts and repayment durations.
- Seeking Expert Advice: Consult with a financial advisor or credit counselor for personalized guidance tailored to individual circumstances.
- Responsible Borrowing Practices: Prioritize the establishment of a robust financial plan that includes emergency savings and a detailed budget.
Recommended Resources
To further enhance understanding and support informed decisions, access these valuable resources:
Utilizing these resources alongside the information presented in this document will empower individuals to make informed decisions regarding low-interest personal loans.
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, low-interest personal loans can be a helpful financial tool if used responsibly. Thorough research, understanding the terms, and comparing options are essential before making a decision. This guide provides a framework for making an informed choice about your financial needs.